A risk-free fetal genetic test
Introduction
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is based on the detection of placental DNA circulating in the mother’s blood. This placental genetic material is compared with the mother’s DNA for analysis.
What does the test involve
This test analyses placental DNA present in the mother’s blood. It is recommended from the 12th week of pregnancy onwards and requires only a standard blood test from the mother.
It enables screening for the most common chromosomal abnormalities: trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), with a detection rate of almost 99.9%, and trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edwards syndromes, respectively), with a detection rate of nearly 98%.
In addition, the test can determine the sex of the fetus and identify abnormalities in the number of sex chromosomes, as well as syndromes caused by smaller losses of genetic material known as microdeletions.
Results are reported as low risk or high risk. A low-risk result corresponds to a risk below 1 in 10,000. If the result is high risk, as this is a screening rather than a diagnostic test, confirmation with an invasive diagnostic technique (an amniocentesis) is required before any decisions are made regarding the pregnancy.
Available options
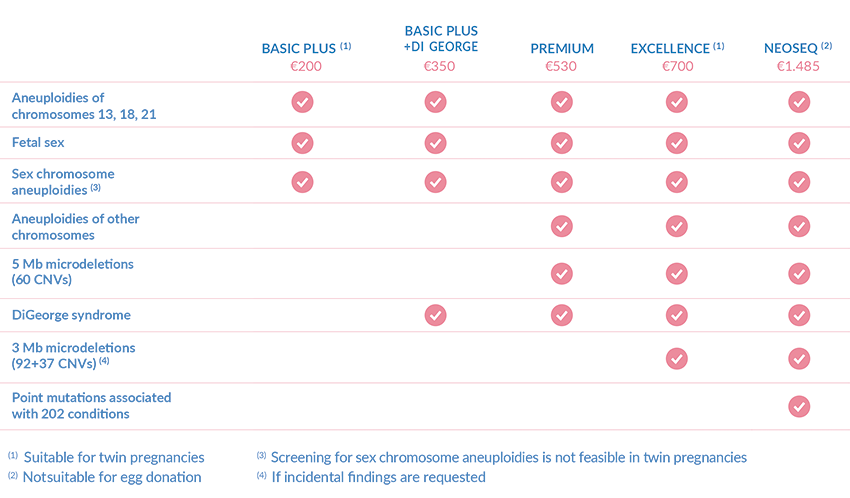
- Basic plus (1) : detects the most common chromosomal abnormalities Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13). In addition to trisomies 13, 18 and 21 and fetal sex determination, it can detect sex chromosome abnormalities (3), such as Turner syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome, which may be associated with specific health conditions.
- Basic plus + DiGeorge: detects trisomies 13, 18 and 21, fetal sex, sex chromosome abnormalities (3) and DiGeorge syndrome, the genetic condition with the highest incidence after Down syndrome (1 in 2,000 births).
- Premium: analyses all chromosomes and a total of 60 microdeletion/microduplication syndromes, as it analyses DNA defects at a resolution greater than 5 Mb. It also includes DiGeorge syndrome.
- Excellence (1) : in addition to all the abnormalities covered by previous tests, this option analyses fetal DNA at much higher resolution (3 Mb), enabling the detection of syndromes caused by much smaller losses or gains of genetic material (microdeletions or microduplications). It can detect up to 92 + 37 different genetic conditions (4), including DiGeorge syndrome.
- NeoSEQ (2) : the most comprehensive option. In addition to all the abnormalities and syndromes associated with microdeletion/microduplication syndromes listed above, it detects pathogenic variants associated with more than 200 severe dominant monogenic diseases, for which no other prenatal test is currently available.
(1) Suitable for twin pregnancies.
(2) Not suitable for egg donation pregnancies.
(3) Screening for sex chromosome aneuploidies is not feasible in twin pregnancies.
(4) If incidental findings are requested.
Advantages
- Non-invasive: the test is performed on a maternal blood sample obtained through a routine blood test.
- Early detection: it allows chromosomal abnormalities to be detected by week 12 of pregnancy.
- 99.9% sensitivity for trisomy 21 (Down syndrome): the prenatal test offered at Dexeus Mujer has higher sensitivity for Down syndrome detection than other traditional prenatal screening tests used in public hospitals and private centres.
- No risk. Unlike other prenatal diagnostic tests, it poses no risk to either the mother or the fetus.
- Suitable for twin pregnancies, IVF and egg donation. It is appropriate for both singleton and twin pregnancies, as well as IVF and egg donation pregnancies.
Who is it for
Non-invasive prenatal testing can be performed on any pregnant woman who wishes to obtain the most comprehensive information possible about her unborn baby’s health.

Results
Results are available about 8–10 working days after the maternal blood sample is analysed, except for the NeoSEQ test, which takes around 25 days, as it includes analysis of additional diseases caused by single-gene genetic changes.
Results are presented as high risk or low risk.
However, a high-risk result is not conclusive. Your gynaecologist will review your case and advise whether an invasive prenatal diagnostic procedure (such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling) is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
For further details, Dexeus Mujer has a specialised unit that provides genetic counselling.
Why choose us
Our team of geneticists can provide comprehensive information on genetic diseases and expert guidance on interpreting test results.
We are pioneers in prenatal diagnostic techniques, a leading centre for high-risk pregnancies and one of the few private centres with a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Our expert committee meets weekly to assess each case individually and define the most appropriate course of action.
We are at the forefront of genomic medicine technology and among the first private gynaecological centres to establish a Medical Genetics Unit.
Testimony
Silvia, 42 years old. Barcelona
"I felt very reassured after taking the test. It was my first child and, because of my age, I had many concerns, but it is absolutely worth it - just a simple blood test. Plus, I was able to find out the baby’s sex very early on. Knowing everything was fine allowed me to enjoy a peaceful pregnancy."
Frequently asked questions
What is the non-invasive prenatal test?
It is a genetic test performed using a maternal blood sample to detect possible chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus without posing any risk to the pregnancy.
What does the non-invasive prenatal test detect?
The test mainly detects the most common trisomies, such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), as well as abnormalities of the sex chromosomes and specific microdeletions (depending on the test version).
Who is this test for?
It is intended for pregnant women seeking a safe, accurate, and risk-free test for the fetus. It is especially recommended in cases of family history, advanced maternal age, or inconclusive results from first-trimester combined screening.
When can the test be performed?
The test can be carried out from the 10th week of pregnancy, as there is sufficient cell-free fetal DNA in the maternal blood at this stage for analysis.
What are its advantages compared to other prenatal tests?
It is a safe and non-invasive test with high reliability (over 99%) for detecting trisomies, without the need for amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, thus avoiding risks to the fetus.
Are additional tests necessary if the result is normal?
In most cases, no. However, the test does not fully replace ultrasound examinations or comprehensive medical follow-up during pregnancy. If there are other clinical concerns, the medical team may recommend further tests.


